【Java3】线性表
🗓 2016年06月18日 📁 文章归类: Java
版权声明:本文作者是郭飞。转载随意,标明原文链接即可。
原文链接:https://www.guofei.site/2016/06/18/java3.html
Array
- 数组分配连续的内存空间
- 数组的长度是固定的
- 数组中的元素可以是一个自定义对象
// 数组的声明
数据类型[] 数组名; // 常用的形式
数据类型 数组名[]; // 这种是为了和其它语言保持一致
// 数组的创建
// 方法1. 先声明后创建
数据类型[] 数组名;
数组名 = new 数据类型[数组长度];
// 例:
int[] arr;
arr = new int[10];
// 方法2 声明时创建
数据类型[] 数组名 = new 数据类型[数组长度]
int[] arr=new int[10];
// 数组的初始化
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5,6,};
数组的使用
arr[0]; // 取数
arr.length; // 长度
arr[1] = 1; // 赋值
例子:
int[] intArray = new int[5];
String[] strArray = new String[5];
float[] floatArray = new float[3];
char[] ch = {'a', 'b', 'c', 'd'};
下面展示对象构成的数组是如何使用的:
// DataType.java
public class DataType {
public int a=1;
public String b="dataType";
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arraySize = 5;
DataType[] myArray = new DataType[arraySize]; // 定义了一个空 array
System.out.println(myArray.getClass());
// 第一种循环
for (int i = 0; i < myArray.length; i++) {
myArray[i] = new DataType(); // 填充这个空 array
}
// 数组作为输入和输出
DataType[] myArray1 = myArrayFunc(myArray);
// 第二种循环: foreach 循环
for (DataType element : myArray1) {
System.out.println(element.a);
}
}
// 数组作为函数输入值 + 数组作为函数返回值
public static DataType[] myArrayFunc(DataType[] inputs) {
return inputs;
}
}
以上代码展示了
- 如何创建一个 array
- 如何填充一个 array
- 两种循环方法
- array 如何作为函数的输入,如何作为函数的输出
下面展示了一些 array 方法
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] myArray1 = new int[5];
int[] myArray2 = new int[5];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
myArray1[i] = i;
myArray2[i] = i;
}
// Arrays.equals 用来判断两个 array 是否完全相等
boolean totalEqual = Arrays.equals(myArray1, myArray2);
System.out.println(totalEqual);
// Arrays.fill 用来用指定类型填充 array
Arrays.fill(myArray1, 1);
for (int elements : myArray1) {
System.out.println(elements);
}
// Arrays.sort 用来升序排列
Arrays.sort(myArray2);
for (int elements : myArray2) {
System.out.println(elements);
}
}
}
Collection
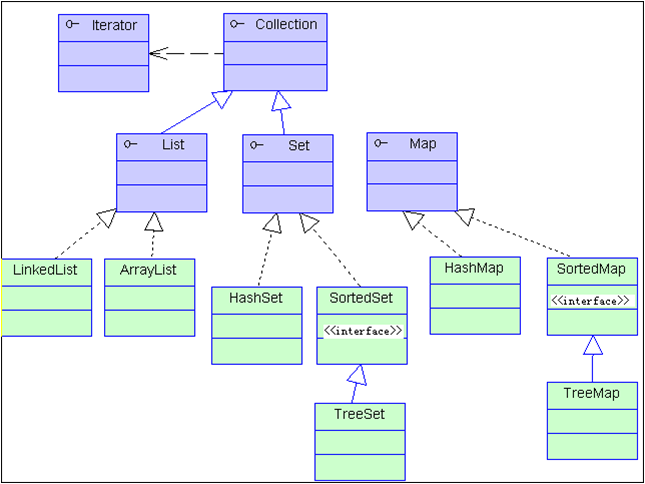
- List:ArrayList
- Queue:LinkedList
- Set无序、不允许重复:HashSet
- Map:HashMap
实验发现,ArrayList,HashSet 都可以存放对象。
- Iterator接口
// 该接口允许遍历集合中的所有元素,一共有三个方法: public boolean hasNext():判断是否还有下一个元素。 public Object next():取得下一个元素,注意返回值为 Object,可能需要类型转换。如果不再有可取元素,则抛出NoSuchElementException异常。在使用该方法之前,必须先使用hasNext()方法判断。 public void remove():删除当前元素,很少用。 - Collection接口
// 最基本的集合接口,一个Collection代表一组Object // public boolean add(Object?o):往集合中添加新元素。添加成功,返回true,否则返回false。 public Iterator iterator():返回Iterator对象,这样就可以遍历集合中的所有元素了。 public boolean contains(Object?o):判断集合中是否包含指定的元素。 public int size():取得集合中元素的个数。 public void clear():删除集合中的所有元素。 // 支持 iterator 方法: Iterator it = collection.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()) { Object obj = it.next(); } - Set集合
// Set 无序存放,主要有如下两个实现:HashSet和TreeSet // HashSet 类按照哈希算法来存取集合中的对象,具有很好的存取性能。当HashSet向集合中加入一个对象时,会调用对象的hashCode()方法获取哈希码,然后根据这个哈希码进一步计算出对象在集合中的存放位置。 // TreeSet实现了SortedSet接口,可以对集合中的元素排序。如何排序的内容请参考其他文档,这里不做详述。 - List集合
// List是一种有序集合, // List允许有重复元素。当然,也有List的实现类不允许重复元素的存在。 // 同时,List还提供一个listIterator()方法,返回一个ListIterator接口对象,和Iterator接口相比,ListIterator添加元素的添加,删除,和设定等方法,还能向前或向后遍历,- ArrayList类->List
// 1. 动态数组,也是在内存中连续, // 2. 可以改变大小。每个ArrayList实例都有一个容量(Capacity),即用于存储元素的数组的大小。这个容量可随着不断添加新元素而自动增加,但是增长算法并没有定义。当需要插入大量元素时,在插入前可以调用ensureCapacity方法来增加ArrayList的容量以提高插入效率。 // 3. 尾部插入和删除效率非常高 // 4. 允许所有元素,包括null // size,isEmpty,get,set方法运行时间为常数。但是add方法开销为分摊的常数,添加n个元素需要O(n)的时间。其他的方法运行时间为线性。 // ArrayList没有同步 // 主要方法: public boolean add(Object?o):添加元素 public void add(int index, Object element):在指定位置添加元素 public Iterator iterator():取得Iterator对象便于遍历所有元素 public Object get(int?index):根据索引获取指定位置的元素 public Object set(int index,Object element):替换掉指定位置的元素 // 排序方法: Collections.sort(List list):对List的元素进行自然排序 Collections.sort(List list, Comparator comparator):对List中的元素进行客户化排序 - LinkedList类->List
// 允许null元素。 // 提供额外的get,remove,insert方法在LinkedList的首部或尾部。这些操作使LinkedList可被用作堆栈(stack),队列(queue)或双向队列(deque)。 // LinkedList没有同步方法。如果多个线程同时访问一个List,则必须自己实现访问同步。一种解决方法是在创建List时构造一个同步的List: List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList(...));
- ArrayList类->List
- Map
// Map是一种把键对象和值对象进行映射的集合,它的每一个元素都包含一对键对象和值对象。 // 向Map添加元素时,必须提供键对象和值对象。 // 从Map中检索元素时,只要给出键对象,就可以返回对应的值对象。 // 键对象不能重复,但值对象可以重复。 // Map有两种常见的实现类:HashMap 和 TreeMap public Object put(Object key, Object value):插入元素 public Object get(Object?key):根据键对象获取值对象 public Set keySet():取得所有键对象集合 public Collection values():取得所有值对象集合 public Set entrySet():取得Map.Entry对象集合,一个Map.Entry代表一个Map中的元素- HashMap
// HashMap按照哈希算法来存取键对象,有很好的存取性能。 // 和HashSet一样,要求当两个键对象通过equals()方法比较结果为 true 时,这两个键对象的 hashCode() 方法返回的哈希码也一样。 - TreeMap
// TreeMap实现了SortedMap接口,能对键对象进行排序。同TreeSet一样,TreeMap也支持自然排序和客户化排序两种方式。 // 要求实现 Comparable 接口,并且 comparedTo() 和 euqals() 的结果一致
- HashMap
关于List性能:
- ArrayList 基于动态数组的数据结构,LinkedList 基于链表
- 对于 get 和 set,ArrayList优于LinkedList,因为ArrayList可以随机定位,而LinkedList要移动指针一步一步的移动到节点处。
- 对于新增和删除操作add和remove,LinkeList比较占优势,只需要对指针进行修改即可,而ArrayList要移动数据来填补被删除的对象的空间。
ArrayList
构造
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
// 新建一个空的
ArrayList<String> arr1 = new ArrayList<String>();
// 新建,并指定初始容量为3
ArrayList<String> arr2 = new ArrayList<String>(3);
// 从 Array 新建
String[] arr = {"a", "b", "c"};
ArrayList<String> arrLst = new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList(arr));
// 新建
ArrayList<String> arrLst = new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c"));
ArrayList<String> objList = new ArrayList<String>(Collections.singleton("新建一个单条记录的ArrayList"));
增
arrLst.add("d"); // 添加,返回 boolean
arrLst.add(1,"d"); // 添加到指定位置
arrLst.addAll(Arrays.asList("1", "2", "3")); // 把另一个 Collection 中的元素添加进去
boolean isSucceed = arrLst.addAll(1, Arrays.asList("1", "2", "3"));
删
arrLst.clear(); // 清空
arrLst.remove("b"); // 移除某个元素,
// 如果有重复元素,只会移除一个
// 如果成功移除,返回 true;否则返回 false
arrLst.remove(1); // 移除 index = 1 的某个元素
改
arrLst.set(1,"x");
查
arrLst.get(1); // 获取某个 index 对应的元素
arrLst.contains("b"); // 是否包含
arrLst.isEmpty(); // 是否为空
其它
arrLst.size(); // 类似 lenght
arrLst.clone();
String[] arr= (String[]) arrLst.toArray(); // 转为数组
Iterator // 迭代器方法
list 接口
arrLst.indexOf(1); // 返回某个值
arrLst.indexOf("b"); // 返回某个对象在list中的位置,重复的返回第一个
arrLst.sort(Comparator.naturalOrder()); // 排序
例子:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> myArray = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
myArray.add(i);
}
System.out.println(myArray);
Iterator<Integer> nameIterator = myArray.iterator();
// remove
while (nameIterator.hasNext()) {
Integer a = nameIterator.next();
System.out.println(a);
if (a == 3) {
nameIterator.remove();
}
System.out.println(myArray);
}
// forEachRemaining()方法对集合中尚未由迭代器访问的每个元素执行操作。
// 迭代器是一次性对象。不能重置。要再次遍历,需要创建一个新的Iterator。
Iterator<Integer> nameIterator2 = myArray.iterator();
nameIterator2.forEachRemaining(System.out::println);
}
}
以上代码展示了
- 2种借用 iterator 的遍历方法
- remove 方法
LikedList
用链表实现的,使用方式与 ArrayList 差不多,下面只记不一样的地方
构造
LinkedList<String> linkedListTmp = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<>(Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c"));
增
// add, addAll 跟上面一样
public void addFirst(E e),添加到第一个元素;
public void addLast(E e),添加到最后一个元素;
删
// clear, remove 同上
linkedList.removeFirst();
linkedList.removeLast();
改,set
查
// contrains, get, indexOf 同上
linkedList.getLast();
linkedList.getFirst()
HashSet
- 无序
- 不允许重复
- 底层是 HashMap
HashSet<String> hashSet1 = new HashSet<String>(3);
HashSet<String> hashSet1 =new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c"));
// 来自 Set 接口方法
hashSet1.add("a");
hashSet1.clear();
hashSet1.contains("b"); // 返回 boolean 类型
hashSet1.containsAll(hashSet2); // 是否是子集,返回 boolean 类型
hashSet1.equals(hashSet2); // 元素是否相等
hashSet1.isEmpty()
hashSet1.remove("c")
hashSet1.size()
iterator
toArray //转数组
集合操作:
// 并集,结果存到 s1
s1.add(s2);
// 交集,结果存到 s1
s1.retainAll(s2);
// 差集,结果存到 s1
s1.removeAll(s2);
// boolean 类型,是否是子集
s2.containsAll(s1)
// Notice.java
public class Notice {
public String name;
public String contents;
public Notice(String name,String contents){
this.name=name;
this.contents=contents;
}
public String toString(){
return this.name+" 公告板显示:"+this.contents;
}
}
import java.util.HashSet; // HashSet
import java.util.LinkedHashSet; // 有序的 HashSet
import java.util.Set;
Notice n1 = new Notice("统计系通知","考试进行中");
Notice n2 = new Notice("数学院通知","考试周");
Notice n3 = new Notice("数学院通知","考试周");
Set s1 = new HashSet();
s1.add(n1); // 1. 元素可以是自定义的对象
s1.add(n2);
s1.add(n3);
System.out.println(s1); // 2. 默认按照对象本身来做去重,因此有3个元素。
// 如果想自定义去重,可以重写 hashCode() 和 equals()
为了改变 HashSet 的去重逻辑,可以重写 hashCode() 和 equals()
// Notice.java
public class Notice {
public String name;
public String contents;
public int duration;
public Notice(String name, String contents, int duration) {
this.name = name;
this.contents = contents;
this.duration = duration;
}
public String toString() {
return this.name + " 公告板显示:" + this.contents;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + duration;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((contents == null) ? 0 : contents.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if(obj.getClass()== Notice.class){
Notice n_tmp=(Notice) obj;
return (n_tmp.name.equals(name))&&(n_tmp.duration==duration)&&(n_tmp.contents.equals(contents));
}
return false;
}
}
Notice n1 = new Notice("统计系通知","考试进行中",1);
Notice n2 = new Notice("数学院通知","考试周",2);
Notice n3 = new Notice("数学院通知","考试周",2);
Set<Notice> s1 = new HashSet<Notice>(); // 1. 泛型。为了防止类不一致导致的错误
s1.add(n1);
s1.add(n2);
s1.add(n3);
System.out.println(s1); // 2. 这样,就只剩下2个元素了。
HashMap
HashMap<String,Integer> hashMap= new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("key1",1); // 添加
hashMap.putAll(hashMap2); // 批量添加
hashMap.get("key1"); // 获取
hashMap.replace("key1", 2); // 修改
hashMap.remove("key1"); // 删除
hashMap.clear();
hashMap.containsKey("key1"); // 是否包含
hashMap.containsValue("key1"); // 是否包含
hashMap.size()
hashMap.remove("key1"); // 返回 key1 对应的 value,并将其移除
Set<String> keySet= hashMap.keySet(); // 返回 key
Collection valueSet = hashMap.values(); // 返回 value
System.out.println(valueSet);
entrySet() // 返回所有键值对
其它类型
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
FastJson
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.73</version>
</dependency>
使用
String jsonStr="{\"id\": 1001, \"name\": \"张三\", \"age\": 24, \"action\":[\"add\", \"sub\"]}";
JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(jsonStr);
System.out.println(jsonObject.get("id"));
JSONArray jsonArray = (JSONArray) jsonObject.get("action");
System.out.println(jsonArray);
JSONArray jsonArray1 = JSON.parseArray("[\"a\", \"b\"]");
stream
- stream不存储数据,而是按照特定的规则对数据进行计算,一般会输出结果。
- stream不会改变数据源,通常情况下会产生一个新的集合或一个值。
- stream具有延迟执行特性,只有调用终端操作时,中间操作才会执行。
创建
三种方法创建stream
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
// 1、通过 java.util.Collection.stream() 方法用集合创建流
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c");
// 创建一个顺序流
Stream<String> stream = list.stream();
// 创建一个并行流
Stream<String> parallelStream = list.parallelStream();
// 2、使用java.util.Arrays.stream(T[] array)方法用数组创建流
int[] array={1,3,5,6,8};
IntStream stream = Arrays.stream(array);
// 3、使用Stream的静态方法:of()、iterate()、generate()
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);
Stream<Integer> stream2 = Stream.iterate(0, (x) -> x + 3).limit(4);
stream2.forEach(System.out::println); // 0 2 4 6 8 10
Stream<Double> stream3 = Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(3);
stream3.forEach(System.out::println);
- stream 是顺序流
- parallelStream 是并行流,如果流中的数据量足够大,并行流可以加快处速度
- stream 可以转 parallelStream:
Optional<Integer> findFirst = list.stream().parallel().filter(x->x>6).findFirst();
用法
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public List<String> strList = Arrays.asList("adnm", "admmt", "pot", "xbangd", "weoujgsd");
public List<Integer> intList = Arrays.asList(7, 6, 9, 3, 8, 2, 1);
forEach
intList.stream().filter(x -> x > 6).forEach(System.out::println);
findFirst, findAny
Optional<Integer> findFirst = intList.stream().filter(x -> x > 6).findFirst();
Optional<Integer> findAny = intList.parallelStream().filter(x -> x > 6).findAny();
findFirst.get()
collect
List<Integer> intList2 = intList.stream().filter(x -> x > 7).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 还可以存为其它类型
Set<Integer> intSet = intList.stream().filter(x -> x > 7).collect(Collectors.toSet());
Map<Integer,Integer> intMap = intList.stream().filter(x -> x > 7).collect(Collectors.toMap(x->x+1, x->x+3));
anyMatch
boolean anyMatch = intList.stream().anyMatch(x -> x < 6);
filter(上面有)
聚合(max/min/count)
// 最长字符串
Optional<String> maxStr = strList.stream().max(Comparator.comparing(String::length));
// 最大整数
Optional<Integer> maxInt = intList.stream().max(Integer::compareTo);
// 自定义排序
Optional<Integer> maxInt2 = intList.stream().max(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1.compareTo(o2);
}
});
映射(map/flatMap)
// 大写
strList.stream().map(String::toUpperCase)
// 运算
intList.stream().map(x -> x + 10)
flatMap
// 功能:把字符串切开,平摊成另一个 list
List<String> strListNew = strList.stream().flatMap(s -> {
String[] split = s.split("");
Stream<String> s2 = Arrays.stream(split);
return s2;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
reduce
// 求和方式1
Optional<Integer> sum = intList.stream().reduce((x, y) -> x + y);
// 求和方式2
Optional<Integer> sum2 = intList.stream().reduce(Integer::sum);
// 求和方式3
Integer sum3 = intList.stream().reduce(0, Integer::sum);
// 求乘积
Optional<Integer> product = intList.stream().reduce((x, y) -> x * y);
// 求最大值方式1
Optional<Integer> max = intList.stream().reduce((x, y) -> x > y ? x : y);
// 求最大值写法2
Integer max2 = intList.stream().reduce(1, Integer::max);
聚合函数
// 求 count
Long cnt = intList.stream().filter(x -> x > 6).collect(Collectors.counting());
// 求平均值
double avg= intList.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(x->x));
// 求最大值
Optional<Integer> max=intList.stream().collect(Collectors.maxBy(Integer::compare));
// 求和
Integer sum = intList.stream().collect(Collectors.summingInt(x->x));
字符串:join
String strJoined=strList.stream().collect(Collectors.joining("->"));
分组
Map<Boolean,List<Integer>> part=intList.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(x->x>6));
//>{false=[6, 3, 2, 1], true=[7, 9, 8]}
// 更多用法见原文
排序
List<Integer> intListOrdered=intList.stream().sorted(Comparator.reverseOrder()).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 更多用法见原文
合并、去重、限制、跳过等操作
List<Integer> intList2 = Arrays.asList(9,7, 6, 9, 3, 8, 2, 1);
List<Integer> intListNew=
Stream.concat(intList.stream(),intList2.stream()). // 合并两个 stream
distinct(). // 去重
limit(5). // 只取前5个
skip(2). // 删除其中的 2
collect(Collectors.toList()); // 输出
参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/299064490
其它代码
// 不换行输出
System.out.print
// 等待键盘输入
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
// sc.next() //字符串
System.out.println(n);
您的支持将鼓励我继续创作!
